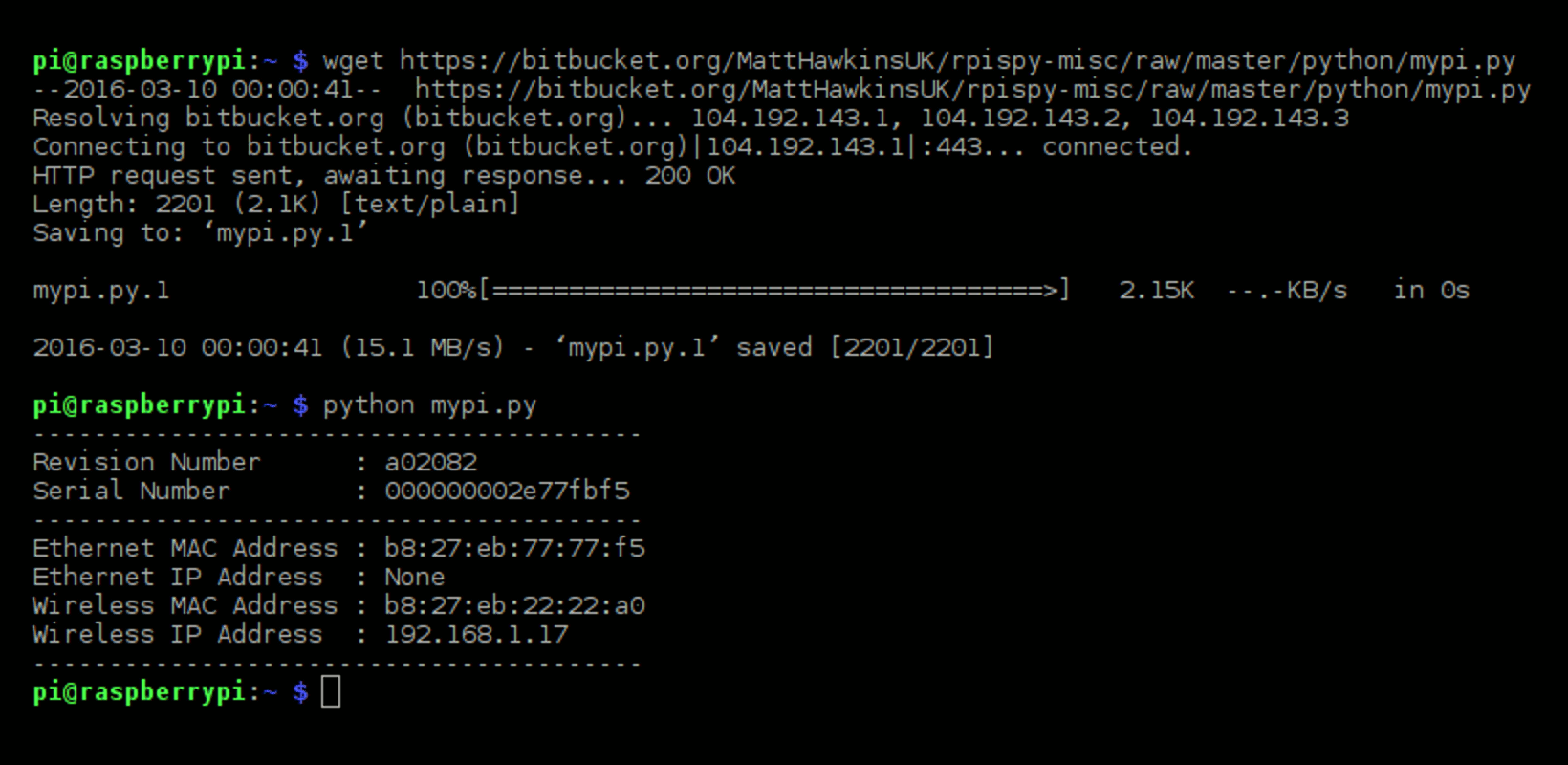
Raspberry Pi Imager is the recommended option for most users to write images to SD cards.
On this tutorial I show you how to run Mac OS 9 on your Raspberry PI, I have also included a compiled version of pearpc if you feel adventurous enought to ru. Raspbian OS has greatly been reviewed, and there are numerous online guidelines to set up or troubleshoot the Raspberry Pi 3 operating system. Comes with the special version of Minecraft 2. RISC OS Pi for Raspberry Pi 2, 3, & 4. RISC OS Pi was first launched in 1987, and it was designed by the same manufacture of an ARM microprocessor.
- Connect to your Raspberry Pi Using VNC If you’re more comfortable working in the Raspberry Pi Desktop environment, you can use a program called VNC to login and run programs on the Raspberry Pi. First, install VNC Viewer on your Mac.
- On this tutorial I show you how to run Mac OS 7 color on your Raspberry PI, I have also included a compiled version for Windows. I had so much fun while getting this working and spend more time then I care to admit playing old games. Thanks for the view!! Equipment List: Raspberry Pi 3 Amazon Ebay.
- If you’re looking for an open-source OS for Raspberry Pi to make things interesting to learn and educate kids, Kano OS is a good choice. It’s being actively maintained and the user experience for the desktop integration on Kano OS is quite simple and fun for someone to play and make kids learn from it.

Determine SD device
- Insert the SD card in the slot or connect the SD card reader with the SD card inside.
Command Line
diskutil listExample (the SD card is /dev/disk2 - your disk and partition list may vary):
Graphical / Disk Utility
- From the Apple menu, choose 'System Report', then click on 'More info...'.
- Click on 'USB' (or 'Card Reader' if you are using a built-in SD card reader), then search for your SD card in the upper right section of the window. Click on it, then search for the BSD name in the lower right section.It is in the form
diskN(for example,disk4).Record this name. - using Disk Utility, unmount the partition.Do not eject it.
Copy the image
Command Line
Note: The use of the dd tool can overwrite any partition of your machine.If you specify the wrong device in the instructions, you could overwrite your primary Mac OS partition!
The disk must be unmounted before copying the image
Copy the image
Replace
Nwith the number that you noted before. Note therdisk('raw disk')instead ofdisk, this speeds up the copying.This can take more than 15 minutes, depending on the image file size.Check the progress by pressing Ctrl+T.
If the command reports
dd: /dev/rdiskN: Resource busy, you need to unmount the volume firstsudo diskutil unmountDisk /dev/diskN.If the command reports
dd: bs: illegal numeric value, change the block sizebs=1mtobs=1M.If the command reports
dd: /dev/rdiskN: Operation not permitted, go toSystem Preferences->Security & Privacy->Privacy->Files and Folders->Give Removable Volumes access to Terminal.If the command reports
dd: /dev/rdiskN: Permission denied, the partition table of the SD card is being protected against being overwritten by Mac OS. Erase the SD card's partition table using this command:That command will also set the permissions on the device to allow writing.Now issue the
ddcommand again.
Eject
After the dd command finishes, eject the card:
“I know what would be a fun little project for Think Retro,” I thought one day, like the prize chump I am: “installing a classic Mac OS onto a Raspberry Pi.”
The key words there were “fun” and “little,” but as the hours ticked by it was clear that “little” was laughably optimistic, and “fun” was true only in the way that a day at boot camp is fun: you know it’s good for you to be pushed out of your comfort zone and exercise bits of your anatomy that are usually blissfully underused, but you only really feel it was actually fun once you’re back at home, soaking in the tub and with a glass of port within easy reach.
The problem, of course, is that you can’t install Mac OS directly onto the Raspberry Pi—it wasn’t built for that platform—but I wanted Mac OS on the Pi because it seemed like there was a nice echo not just in how both the Pi and Mac played a part in democratizing computing but also in their hardware capabilities. Clearly, even a Rev. A Raspberry Pi is technically far more powerful than was the original Macintosh, but there’s still something pleasing to me about doing it this way rather than just installing an emulator on my 4GHz Core i7 iMac 5K.
Something of the spirit of Woz and the Apple I and II seems to live on in the Raspberry Pi.
And besides, to confuse the early Apple computers a bit, something of the spirit of Woz and the Apple I and II seems to live on in the Raspberry Pi. Plus, I could bust out my ADB to USB adapter—or so I fondly imagined—so that I could use a proper old-skool Apple keyboard and mouse with it.
Anyway. At this point, I was lulled into a false sense of security when my initial research threw up phrases like “easy” and “prebuilt binary.” The implication was that other people had done the hard work of getting Mac OS to run in emulation on the Raspberry Pi and all I had to do was run a script. And indeed, ultimately, it proved—but I had failed to take into account my idiocy.
Actually, that’s unfair. I’m not an idiot, I’m just someone whose first experiences with computers involved slotting a tape into a deck and switching them on and who then leapfrogged straight to GUIs. I’ve never spent much time in the command line.
Thus, when I sat down to install Mac OS on my Raspberry Pi, I kept getting stumped by the most basic things. I know there will be people far more experienced and knowledgeable than me (and also, what’s worse, much less so) who will be baffled by how anyone calling themselves a technology journalist can be so perplexed by such fundamental tasks, but like me, you might have found this often if you’ve dabbled in Linux or with the Pi.
For example, this first comment on this Reddit thread at /r/VintageApple suggests that you just issue a few commands and everything’s done for you. And this is true. It’s just that, having installed Raspbian on my Pi using the beginner-friendly NOOBS method, when it’s booted I am first faced with the question of where I issue those commands.
OK, so I’m not so green that I don’t think of launching a Terminal window. SoI do that, type in the first line, and hit Return—even this being an assumption—and I get an error about not being root. From this vantage point as I write these words, some hours and several different install method attempts later, I assume that I ought instead to have prefixed the command with “sudo,” but this is the kind of thing that kept stopping me in my tracks.
“There is a prebuilt binary of Mini vMac and I think Basilisk in the RetroPie image,” the Reddit thread burbles happily. “Recommend because nice front end.” Well that sounds like just the ticket. I Google RetroPie, which turns out to be a collection of emulated hardware, heavy on vintage games consoles, and… well, look, basically, me documenting all the things I tried and which, for a glitteringly broad range of reasons, failed to get working would be as turgid for you to read as it was for me to live through.
There was a lot of this kind of thing…
Raspberry Pi Mac Os 9
…and occasional glimpses of these frightful old pseudo-GUI configuration pages which after so long lost in the command-line were like a goblet of urine to a man wandering in the desert: vile, but a bewitching reminder of what your life could be like when this was all over.
I broke for lunch after one of my attempts, which should have been simple—installing a ready-made version of RetroPie onto an SD card—failed because even though I didn’t want to use RetroPie for gaming, it refused to load because it couldn’t detect a gamepad, and I didn’t have a compatible one to use with it.I came back after lunch ostensibly refreshed and reinvigorated but as soon as I looked at the infestation of browser tabs strewn over my Mac’s three screens, my scribbled notes, and the dregs of espresso that had powered my morning experimentations, I lost heart, and decided to give up.
I felt bad about this for the rest of the day—disappointed in myself because this should have been within my grasp, and for having caved after only a morning’s effort—until I realized that the kinds of problems I’d been having, indeed the existence of these problems at all, were the very things the Mac was originally designed to banish.
Raspberry Pi Mac Os 7
I will make this work at some point—it will be easier because I’ll both have had this morning’s experience and will have learned from that to allocate some proper time to the project—but for now, I’m happy to reach behind my Classic II and flick a switch whenever I feel the need to potter about in vintage Mac OS. And when I do, I give thanks once again to Apple for making computers that easy.

